e.sunie
2018. 11. 5. 01:17
문제 [6-22]
p.383 String class 표 참고
- charAt(index) : 반환(char)
- s1.equals(" ") :자기자신(s1)과 매개변수("") 가 같으면 true(반환: boolean)
- s1.length : string의 길이 return (반환:int)
|
class EX6_22
{
static boolean isNumber(String str){
if(str==null||str.equals(""))
return false;
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++)
{
char ch=str.charAt(i);
if(ch<'0'||ch>'9')
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
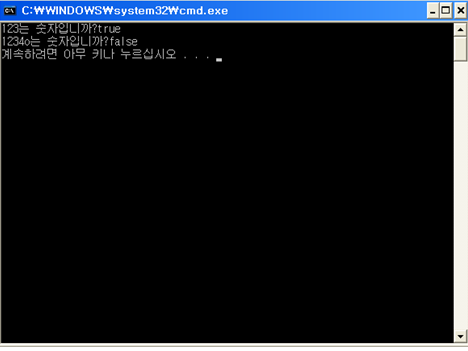
String str="123";
System.out.println(str+"는 숫자입니까?"+isNumber(str)); str="1234o";
System.out.println(str+"는 숫자입니까?"+isNumber(str)); }
} |
 |
isNumber가 static 변수가 아니면 error!
->why?
static은 staic만 부를수 있다 non-static을 불러올수 없음
인스턴스 변수나 메서드는 객체가 꼭 필요! 반면 static은 필요 없으~
커피를 마셨더니 배가 보글보글~~

객체지향개념 2-3 (추상클래스 & 인터페이스 )
6.1 추상클래스
- 추상 메서드 : 구현은 자식클래스에서...
- 추상클래스에서 일반메서드 구현 가능, 일반메서드가 추상메서드 구현 가능
6.2 추상메서드
when : 꼭 필요하지만 자손마다 다르게 구현하게 될 것 같을 때
졸 to the 려
구체적인 내용은 자손클래스에서 구현
how? 추상클래스를 상속받고 난후 상세 구현
shape -> getArea():넓이구하는 메서드(추상) ->computeArea(double,double)
circle rectangle truangle
3.14*r*r, w*h,0.5*b*h
|
abstract class Shape
{
abstract void computeArea(double a, double b);
}
class Circle extends Shape
{
void computeArea(double r1, double r2){
System.out.println("Area of Circle : "+ (3.12*r1*r2));
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape
{
void computeArea(double w, double h){
System.out.println("Area of Rectangle : "+ (w*h));
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape
{
void computeArea(double b, double h){
System.out.println("Area of Triangle : "+ (0.5*b*h));
}
}
class AbstractTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
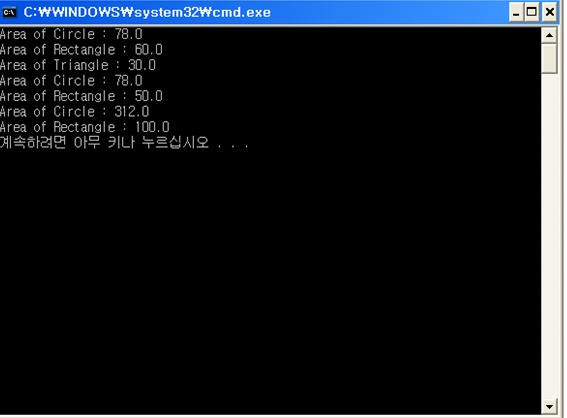
Circle c=new Circle();
c.computeArea(5.0,5.0);
Rectangle r = new Rectangle();
r.computeArea(4.0,15.0);
Triangle t = new Triangle();
t.computeArea(4.0,15.0); Shape s=new Circle();
s.computeArea(5.0,5.0);
s=new Rectangle();
s.computeArea(5.0,10.0);
//배열형태로도 사용가능
Shape[] group =new Shape[2];
group[0]=new Circle();
group[1]=new Rectangle(); group[0].computeArea(10.0,10.0);
group[1].computeArea(10.0,10.0);
}
} |
 |

![]()

